Strategie e pratiche per l'autismo
Senza una deviazione dalla norma, il progresso non è possibile.
Being autistic
How people experience the world varies widely from person to person, but there are some things in common between autistic individuals.
Generally, individuals experience sensory and cognitive processing differently than those not on the autism spectrum, and have differences in social interaction and interpreting other autistics is easier than interacting and communicating with non-autistic.
Some individuals are extremely passionate about a particular topic and like to talk or engage in it for extended periods of time, while others may have very limited language skills. Some autistic people might like loud noise and lots of movement, others might be highly sensitive to noise and don’t like to be touched. Some enjoy a consistent routine and don’t like it to change, while others are more flexible with routines.
Poiché gli individui elaborano il mondo in modo diverso, hanno intuizioni uniche e spesso riescono a vedere le cose in modo diverso dagli altri.
The different perspectives and experiences of the autistic and neurodivergent community are vital to our society and it is important that autistic people are provided the opportunities for their voices to be heard and their differences celebrated. Being autistic also can come with its own set of challenges in experiencing and engaging in the world around them.
It is common for some autistic people to become anxious with changes to their routine or environment. This can make everyday tasks like leaving the house – even popping up to the shops – a difficult exercise.
Alcuni individui sono molto sensibili a particolari rumori o al tatto, per cui trovarsi in luoghi pubblici o in occasioni sociali può essere opprimente e sconvolgente.
Some individuals experience what is known as hypersensitivity – where the senses are heightened and everything is experienced intensely. The opposite of this is hyposensitivity – where the senses only respond to extremes. This can extend to not feeling any pain or only seeing the outlines of objects.
Some autistic people– particularly children – can experience extra complexities with understanding and managing their emotions. This can result in feeling overwhelmed and experiencing meltdowns.

What are the benefits of support and services?
Understanding how autism will impact on you, or your child’s life, allows you to access supports and services that can help manage challenges and build on strengths.
Once you have a diagnosis, it’s common to feel a bit overwhelmed about what to do next. The good news is there are many options for getting assistance. Due to there being so many options it can also be a little overwhelming and can take a while to get your head around what’s best for you, or your child.
Assicuratevi di avere il tempo di documentarvi su ciò che è disponibile e su ciò che meglio si adatta alla vostra situazione specifica. Parlate con i vostri professionisti della salute e non abbiate paura di fare domande finché non sarete sicuri di avere le risposte che vi servono.
A diagnostic report will often provide information regarding strengths and challenges, which can help you develop a support plan – this is basically a plan that combines different therapies and types of supports and services specifically designed to meet you or your child’s needs.
Some areas that supports and services might focus on include daily living, social and community participation, health and wellbeing, lifelong learning, relationships, and choice and control.
Mentre il termine "intervento" si riferisce all'azione o all'utilizzo di una tecnica per cercare di migliorare o sviluppare le competenze in una particolare area, esistono diverse terminologie per queste azioni o attività di sviluppo.
Some common terms for supports and services include:
- Strategie
- Pratiche
- Programmi
- Approcci
- Terapie
- Interventi precoci
Strategies and therapy approaches are generally individually designed to support a single skill or goal. Therapy strategies are used to develop the individual’s skills (using grading, prompt fading and task breakdowns), to adapt their environment to meet their needs or skill level (using visual supports, educating the child’s support people or incorporating environmental changes or the use of equipment), or often a combination of both.
Therapy programs and approaches generally consist of a set of evidence-based practices or principles implemented to achieve impactful learning for the individual’s and their support people for the individuals goals. For example, the Sequential Oral Sensory (SOS) Approach to Feeding intervention program.
Therapy and therapeutic intervention are generally practices or interventions that are provided by allied health professionals including: Speech Therapists, Occupational Therapists, Psychologists, Social Workers, Psychiatrists, and Art and Music Therapists.
Early intervention or Early support refers to therapy support specifically for children under seven years old, and can be put in place as soon as a diagnosis is made, or sometimes earlier when developmental differences are observed.
For more information about key evidence-based practices and strategies for people on the autism spectrum visit our Communication strategies, Behavioural strategies, Sensory strategies, and Social strategies pages in this section.

The value of early support
Children who are diagnosed as autistic at a very young age – that is, before the age of seven – can benefit from what is called ‘early intervention’ or ‘early support’.
Early intervention or support combines therapy practices and supports that help children to develop early skills that can provide the child opportunities to live the life they want. Early intervention support is often provided through play-based therapy, as play is often the most effective way for a child to learn, in conjunction with educational support for the child’s support network including their parents, teachers and peers.
While support can be beneficial at any age, early intervention or support can be important because new skills are much easier to learn when you’re very young.
Questo perché ci sono delle fasi di sviluppo fondamentali che il nostro cervello attraversa nella prima infanzia, e attingere a queste fasi può rendere più facile l'apprendimento di nuove cose.
Pensate che i bambini imparano una seconda lingua o a suonare uno strumento musicale molto più facilmente di un adulto che si cimenta per la prima volta. Questa capacità di apprendimento è legata a ciò che gli scienziati chiamano plasticità cerebrale, che in realtà significa solo la facilità con cui il cervello si sviluppa.
We never lose ‘brain plasticity’ though, so if your child isn’t diagnosed until later in life, support and services can still form an important and necessary part of your child’s development and can have a positive impact on their life at any stage.
And while more research is required on the long-term benefits, initial studies suggest that early intervention or support can lead to more independent and functional communication, independence with daily living skills, and can build a range of other skills that can support quality of life.
What is early support?
La nostra capacità di concentrarci, di assorbire informazioni, di comunicare e di socializzare ha un impatto diretto sulla qualità della nostra vita. Se riusciamo a concentrarci, possiamo imparare nuove cose più facilmente. Se riusciamo a comunicare, possiamo non solo esprimere le nostre esigenze, ma anche creare legami con le persone. Se riusciamo a socializzare, possiamo costruire relazioni significative.
For autistics some or all of these skills can look different, which can make it challenging for others to understand and support children to have their needs met. Early support is designed to develop skills in these, and other areas, so that children develop essential skills early in life.
Early support generally focuses on understanding the child’s individual social and communication skills, along with behavioural and cognitive skills and supporting the development of these areas. This includes things like supporting the child’s ability to focus and attend so it is easier to learn, building language skills in order to communicate functionally and understand language, as well as developing daily living skills.
Early support brings together different therapies, that can assist your child, and are tailored to their unique strengths and challenges.
Early support might be offered by one professional, or may bring together several professionals, either through a service provider, organisation, private or government practice. Some programs can be delivered one on one, in small groups, at home, in a centre, or in the community.
Be sure to engage a professional who is well-trained in the therapy they are providing, and who also sees and responds to your child, and your family’s needs.
How do you choose the right services for your child?
As everyone’s experience of autism is unique, there is no one-size-fits-all service. Knowing your child’s strengths and needs will assist you in finding the right supports and services for them.
There are a wide variety of therapies, strategies and programs available, some backed by scientific studies and others built on anecdotal evidence.
Questo significa che dovete fare delle ricerche per scoprire cosa è meglio per il vostro bambino.
Sembra che per avere successo nella scienza o nell'arte, un pizzico di autismo sia essenziale.
We encourage you to look into the programs and strategies you are considering to see how well researched they are.
Ecco una guida completa all'analisi delle prove scientifiche per le strategie e gli interventi.
È bene anche parlare con i professionisti accreditati per sapere come vengono valutati.
Don’t be afraid to ask questions of the people who are providing support and therapy to you and your family to be certain they are right for your child. Ask for more than anecdotal evidence – that is, more evidence of their effectiveness than personal testimonials, such as research articles.
There is a need for greater research into therapy programs for autistic people to fully evaluate their effectiveness, but some are better researched than others and recommended by professionals.
Beware of any programs that make overly optimistic claims about the results they can achieve. Unfortunately, not all therapy approaches and programs are supportive, and some are based on outdated ideas of autism being something that should be fixed, or are built on ideas about the causes of autism that simply aren’t true. In worst case scenarios, some can be harmful to your child
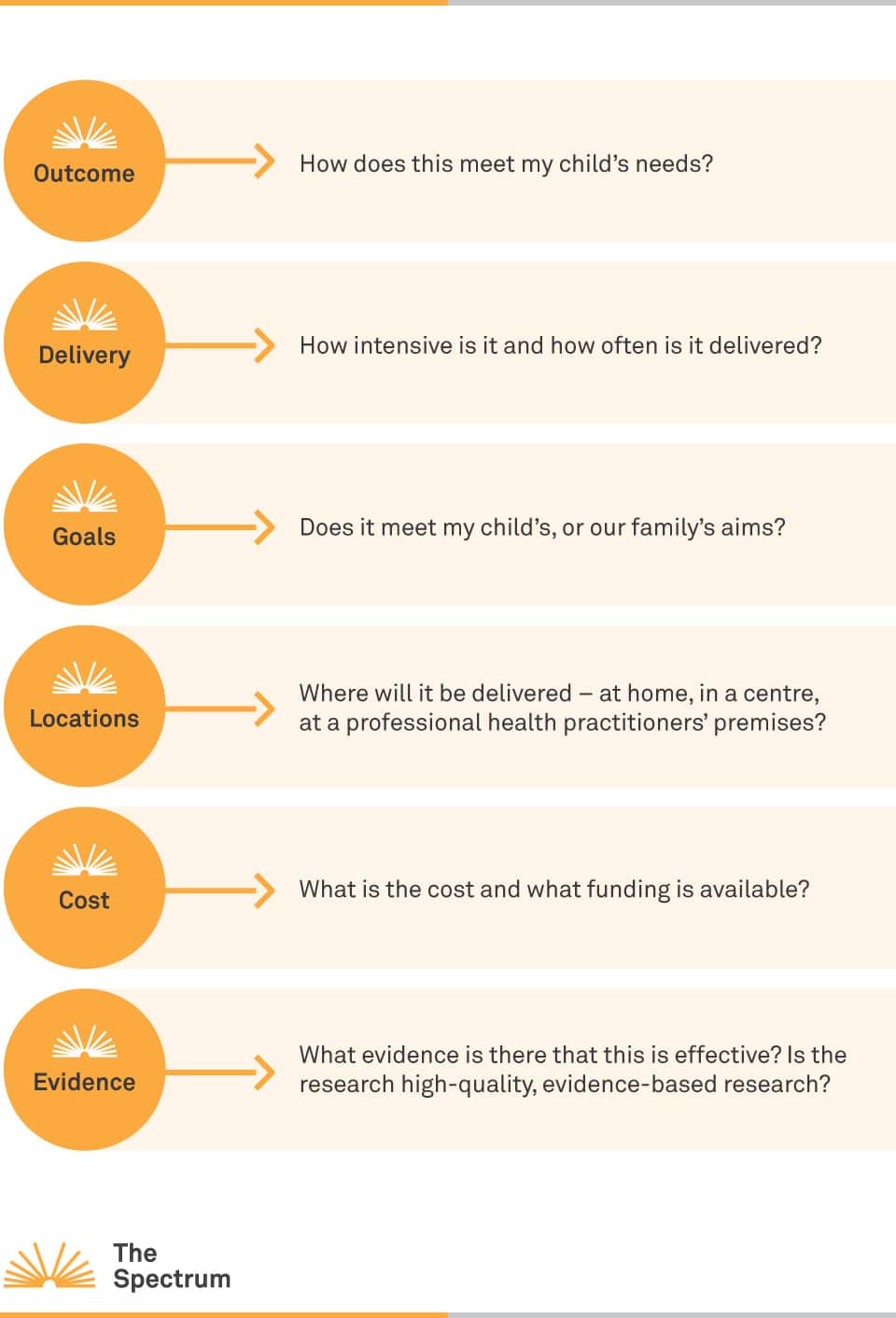
The Early Intervention for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders: ‘Guidelines for Good Practice’ 2012 lists these questions when considering whether a program or therapy approach is for them:
- Quali sono gli obiettivi specifici del programma?
- Ci sono rischi medici o fisici?
- Quali valutazioni dei singoli bambini vengono effettuate prima dell'intervento?
- Qual è la base di evidenza per questo intervento?
- Quali metodi di valutazione sono stati utilizzati per valutare i risultati dell'intervento?
- I proponenti del programma di trattamento hanno un interesse finanziario nella sua adozione?
- Cosa si sa degli effetti a lungo termine di questo trattamento?
- Quanto costa?
- Quanto tempo sarà necessario?
Essenzialmente, dobbiamo chiederci: "Sto facendo la cosa giusta nel modo giusto con la persona giusta al momento giusto nel posto giusto per ottenere il risultato giusto - e sono la persona giusta per farlo? ... e il costo è giusto?" (Cusick, 2001, p. 103).
I servizi che sono stati valutati dal Dipartimento dei Servizi Sociali possono essere trovati qui. Oppure visitate la pagina Supporto e servizi per ulteriori informazioni sui servizi e i supporti nella vostra comunità, specifici per l'autismo.
È inoltre possibile verificare se un fornitore è registrato presso la propria associazione professionale o sul sito web dell'Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency.
The National Disability Insurance Scheme covers early intervention for children 0-6 years. If you are under the NDIS, you can find recommended providers on the website here. Or visit our Financial support page.
What makes early support effective?
In 2020, the Autism CRC produced the Interventions for children on the autism spectrum: A synthesis of research evidence.
The report outlines the core principles that are important to interventions for children on the autism spectrum:
– Holistic assessment – an initial assessment of an individual’s strengths, goals, challenges and preferences
– Individual and family-centred – the child should be placed at the centre of clinical management with the aim to understand and build the capacity of the individual and family to meet a person’s unique needs
– Lifespan perspective – a perspective that acknowledges that people grow and change throughout their lives as they are faced with new tasks, challenges and opportunities, and that capacity around a person will also change over time
– Evidence-based – interventions are most effective and safe when they are based on the best available scientific evidence
Applying an early support can involve everyone assisting your child, including family members, therapists, any childcare providers and/or teachers.
The support should outline your child’s strengths and needs, set goals for the support (agreed by you and your family and those involved) and outline how these goals will be monitored and achieved. Once a support is in place, it should be reviewed every six months to make sure it is continuing to meet your child’s needs.
Una delle cose più importanti è che voi e vostro figlio vi sentiate a vostro agio con la persona o le persone con cui lavorate.
I bambini rispondono meglio alle persone con cui si sentono sicuri e sono più propensi a imparare in un ambiente confortevole.

What types of supports are there?
An intervention is the word used to describe any therapy or service that is used to help support an autistic person’s quality of life.
In genere rientrano in una delle seguenti categorie:
Interventi comportamentali
Come suggerisce il nome, questi tipi di interventi si concentrano sul comportamento, comprendendolo e insegnando poi un nuovo comportamento, più vantaggioso per voi o per vostro figlio.
Insegnano nuovi comportamenti e abilità, di solito intorno a semplici compiti quotidiani, utilizzando tecniche strutturate e progressi graduali.
Gli interventi comportamentali sono tra quelli più comunemente utilizzati, quindi è probabile che siano meglio studiati rispetto ad altri tipi di interventi, anche se è sempre necessario esaminare le ricerche basate sull'evidenza disponibili.
Quando si parla di interventi comportamentali, si può sentire il termine Analisi del Comportamento Applicata ( ABA).
L'ABA è una serie di tecniche e/o strategie utilizzate in alcune terapie comportamentali.
In genere, si tratta di identificare un comportamento o un'abilità, fissare un obiettivo e suddividerlo in piccoli passi da insegnare in modo altamente strutturato.
This might target a specific behaviour, such as washing their hands or saying a particular word. Or it might look at a broader area of self-development, such as improving overall communication abilities.
I progressi vengono misurati nel corso di tutto il percorso, in modo da poter apportare modifiche in base alle esigenze del bambino.
Interventi per lo sviluppo
Piuttosto che concentrarsi sul comportamento esteriore, gli interventi di sviluppo considerano le abilità che una persona deve sviluppare per aiutarla nella vita quotidiana e migliorare la sua capacità di stringere relazioni significative con gli altri.
L'attenzione è spesso rivolta alle abilità emotive e sociali. Ad esempio, le espressioni facciali e i gesti possono essere esagerati per aiutare le persone nello spettro, in particolare i bambini, ad associarli alle emozioni e a imparare a "leggere" le risposte emotive delle persone.
In genere, queste terapie sono guidate dal bambino, nel senso che il terapeuta reagisce al bambino piuttosto che il contrario. Vengono utilizzate tecniche ludiche per incoraggiare le interazioni e ogni risposta del bambino viene considerata significativa.
Nel corso del tempo, i terapisti creano un legame con il bambino, incoraggiando una maggiore interazione. Una volta stabilita una relazione, è possibile iniziare a insegnare abilità specifiche.
Questi tipi di interventi spesso utilizzano anche contesti che fanno parte della vita quotidiana, ma in un modo sicuro e strutturato che fa sentire il bambino sufficientemente al sicuro per apprendere le abilità.
Interventi combinati
Alcune terapie combinano elementi di entrambe le terapie comportamentali e dello sviluppo, o aspetti di altri tipi di interventi.
Questi possono essere molto efficaci in quanto riuniscono le parti rilevanti di diversi stili di intervento, a seconda delle terapie che combinano.
Interventi basati sulla terapia
Ogni singola terapia che si rivolge a un particolare aspetto dello sviluppo di una persona è classificata come intervento basato sulla terapia.
Un esempio è la logopedia per sviluppare le capacità di comunicazione o la terapia occupazionale per sviluppare il movimento fisico. Possono essere incluse anche l'arte e la musicoterapia.
Gli approcci basati sulla terapia sono spesso combinati con altri interventi.
Interventi basati sulla famiglia
As the intensity of therapies – that is, how many hours are spent on them in different environments – can have an impact on their effectiveness, family involvement is a powerful tool.
Family-based interventions put family at the core of any therapies and are built around strong, collaborative relationships between the family and professionals. They often include providing training, support, guidance and information for family members to be able to work with a family member or child on the spectrum.
Interventi medici
Medical interventions are generally prescribed for problems or underlying conditions associated with, but not necessarily caused, by autism, these are considered to be co-occurring conditions.
È molto importante che qualsiasi intervento medico sia prescritto e gestito dal proprio medico o professionista sanitario. Ciò che funziona per una persona può non funzionare per tutti, e tutti i farmaci possono avere effetti collaterali dannosi. Per alcuni farmaci, gli effetti a lungo termine sono sconosciuti.
Interventi alternativi
Le terapie che generalmente non sono ampiamente accettate come parte della medicina occidentale convenzionale o che non sono supportate da prove scientifiche sono classificate come interventi alternativi.
While alternative therapies have become more popular in recent decades, they should be considered with caution, especially in relation to autism. Some alternative therapies – especially those that make wild promises or ridiculous claims to ‘cure’ autism – may do serious harm.
Come per qualsiasi intervento, non fate affidamento su storie personali o lasciate che promesse che sembrano troppo belle per essere vere influenzino il vostro giudizio. Ponete sempre delle domande e fate delle ricerche per capire se la terapia può giovare a voi o a vostro figlio.
Strategie e interventi basati sull'evidenza
Esiste una serie di strategie e interventi che possono essere utilizzati per sviluppare le competenze e sostenere le esigenze delle persone nello spettro autistico.
Questi includono:
- Pratiche informate sulle evidenze: progettate per affrontare una singola abilità o obiettivo di una persona nello spettro autistico.
- Evidence Informed Interventions and Programs: consisting of a set of practices designed to achieve a broad learning or developmental impact on the core characteristics of autism.
In generale, questi programmi sono caratterizzati da:
- Organizzazione: intorno a un quadro concettuale)
- Operativizzazione: procedure manuali
- Intensità: un numero consistente di ore alla settimana
- Longevità: si manifestano nell'arco di uno o più anni
- Ampiezza dell'attenzione ai risultati: sono stati presi in considerazione più risultati, come la comunicazione, il comportamento e la competenza sociale.
The different types of evidence-based interventions currently include:
- Analisi del comportamento applicata (ABA)
- Modello Early Start Denver (ESDM)
- Approccio DIR/Floortime*
- Modello socio-pragmatico dello sviluppo (DSP)
- RDI - Intervento di sviluppo delle relazioni
- Dispositivi di generazione del parlato (SGD) e altri dispositivi di comunicazione aumentativa e alternativa (AAC)
- PECS - Sistema di comunicazione a scambio di immagini
- Ayers Sensory Integration (ASI)
More can be found visiting the Autism CRC Interventions for children on the autism spectrum: A synthesis of research evidence.



